Wireless vs Wired Security Cameras: Which Is Better?
- Бонус за регистрацию онлайн казино
- May 30
- 17 min read
Updated: Jun 2
Securing Your Peace of Mind: A 2025 Guide to Choosing the Right Wireless Security Cameras
Choosing between wireless vs wired security cameras is a crucial decision for effective surveillance. This guide helps you select the best system for your needs in 2025 by comparing six key factors. We'll cover installation, power reliability, video quality, cost, security vulnerabilities, and scalability, giving you the knowledge to protect your home or business. Understanding these elements empowers you to make the right choice for comprehensive security.
1. Installation and Setup Complexity
When choosing between wireless vs wired security cameras, installation and setup complexity is a primary consideration. This factor significantly impacts the initial time investment and potential ongoing maintenance requirements, influencing both cost and convenience. Understanding the nuances of each system's installation process is crucial for making an informed decision tailored to your specific needs and technical capabilities. This fundamental difference can be the deciding factor for many, especially those who are not tech-savvy or prefer a quick and easy setup.

Wireless security cameras, typically using Wi-Fi or cellular connections, generally offer a much simpler and faster installation process. Most battery-powered wireless cameras, like the popular Ring Battery Doorbell, can be installed in minutes with minimal tools, often just a screwdriver. Their wireless nature eliminates the need for running cables, allowing for flexible placement virtually anywhere within the Wi-Fi or cellular range. This ease of installation makes them particularly attractive for renters, DIY enthusiasts, and those looking for a quick security solution. Examples like Arlo wireless cameras showcase this flexibility, allowing users to position cameras strategically without the need for electrical work or professional assistance.
On the other hand, wired security cameras, requiring physical cable connections like Ethernet, coaxial, or power cables, often present a more complex installation process. While a single wired camera might be relatively straightforward to install, more complex systems involving multiple cameras and a Digital Video Recorder (DVR) frequently necessitate professional installation, which can take anywhere from 4 to 8 hours. This involves routing cables through walls and ceilings, potentially requiring drilling holes and careful cable management to maintain a clean and aesthetically pleasing installation. This makes wired systems more suitable for permanent installations where stability and reliability are paramount. They are often preferred for businesses, larger properties, and situations where continuous recording is essential.
The power requirements also differ significantly between the two systems. Wireless cameras can be battery-powered, offering complete freedom from wiring, while others might require a power outlet for continuous operation. Wired cameras, however, necessitate a constant power supply, adding to the installation complexity. Network configuration complexity also varies based on the connection type. Wireless cameras connect to existing Wi-Fi networks, which can sometimes involve configuring network settings and ensuring adequate signal strength. Wired systems might require more intricate network configurations depending on the DVR and network setup.
Pros and Cons of Wired vs Wireless Security Cameras Installation:
Wireless:
Pros: Quick installation, no cable running, flexible placement, minimal tools required.
Cons: Battery replacement needs, potential Wi-Fi interference, signal range limitations.
Wired:
Pros: More stable connection, no battery maintenance, consistent power supply.
Cons: Requires professional installation for complex setups, drilling holes, cable management challenges.
Tips for Successful Installation:
For Wireless: Test Wi-Fi signal strength at intended camera locations before installation to ensure adequate coverage and avoid potential connection issues.
For Wired: Carefully plan cable routes before starting the installation to minimize interference, maintain aesthetics, and ensure efficient cable management.
Consider Hybrid Systems: For complex installations requiring both flexibility and reliability, consider hybrid systems that incorporate both wireless and wired cameras.
Always Test: Regardless of the system chosen, always test all connections and camera functionality before finalizing mounting positions and completing the installation.
Choosing the right security camera system depends heavily on your specific needs and circumstances. If ease of installation and flexibility are top priorities, wireless systems offer a compelling solution. However, if a more robust and reliable connection with continuous power is essential, then wired systems might be the better choice, even with the added installation complexity. Understanding these key differences in installation and setup complexity empowers you to select the security camera system that best aligns with your individual requirements.
2. Power Source and Reliability
Power management represents one of the most critical differences between wireless and wired security cameras, directly impacting system reliability, maintenance requirements, and long-term operational costs. This factor plays a crucial role in determining the suitability of each camera type for different applications, from residential homes to construction sites and temporary event surveillance. Understanding the nuances of power delivery for each system is essential for making informed decisions about your security needs.

Wireless Cameras: The Flexibility of Battery and Solar
Wireless security cameras offer flexibility in placement thanks to their independence from direct electrical wiring. They typically rely on one of three power sources:
Rechargeable Batteries: Many popular wireless models use rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. Battery life varies considerably depending on factors such as video resolution, recording frequency (continuous vs. motion-activated), and environmental conditions. Expect a lifespan ranging from 2-6 months on average. For example, the Ring Stick Up Cam requires charging every 2-3 months with moderate activity, while the Arlo Pro 4 boasts a longer lifespan of 3-6 months under typical usage.
Solar Panels: For a more sustainable and hands-off approach, solar-powered wireless cameras are an excellent option. These cameras utilize small solar panels to trickle-charge their internal batteries, significantly extending their operating time. In sunny climates, solar panels can potentially power wireless cameras indefinitely, eliminating the need for frequent battery swaps. Reolink, for example, offers solar panel add-ons for their wireless camera systems, providing a reliable power source in optimal conditions.
AC Adapters: Some wireless cameras can also be powered by AC adapters, offering a continuous power supply while still maintaining the wireless connectivity advantage for data transmission. This setup provides the reliability of a wired system without the need for extensive wiring infrastructure.
Wired Cameras: The Consistency of Direct Power
Wired security cameras derive their power directly from electrical connections, ensuring a consistent and uninterrupted power supply. This reliability is a major advantage, particularly for critical security applications. Two common methods for powering wired cameras are:
Direct Electrical Connection: This traditional method involves connecting the camera directly to a power outlet using a dedicated power adapter. While reliable, it necessitates running electrical wiring to each camera location.
Power over Ethernet (PoE): PoE technology streamlines installation and reduces cabling costs by delivering both power and data over a single Ethernet cable. This simplifies setup and reduces the need for multiple power outlets. Hikvision, a leading security camera manufacturer, offers a wide range of PoE cameras that leverage this efficient technology.
Pros and Cons: Weighing the Trade-offs
Wireless:
Pros: No electrical wiring needed, portable, can function during power outages (battery-powered models), flexible placement options.
Cons: Regular battery charging/replacement, potential for reduced features to conserve battery life, vulnerability to power failure for AC adapter-powered models, potential for inconsistent performance due to battery limitations.
Wired:
Pros: Continuous power supply, no battery maintenance, consistent performance, generally higher resolution and feature sets.
Cons: Vulnerable to power outages without a Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS), requires electrical connections, potentially higher installation costs.
Tips for Optimizing Power Management:
Wireless:
Set up low-battery notifications to avoid unexpected downtime.
Keep spare batteries charged and readily available.
Consider solar charging for hard-to-reach cameras to minimize maintenance.
Adjust camera settings (resolution, recording frequency) to optimize battery life.
Wired:
Install a UPS backup system to ensure continuous operation during power outages.
Monitor power consumption and adjust camera settings as needed. Consider using PoE switches with power management features.
When and Why to Choose:
Wireless cameras are ideal for renters, DIY enthusiasts, and situations where running wires is impractical or impossible. They excel in temporary setups, such as event security or construction site monitoring. Battery-powered models provide crucial surveillance even during power outages.
Wired cameras are the preferred choice for permanent installations where reliability and continuous operation are paramount. Businesses, homeowners prioritizing comprehensive security systems, and users requiring high-resolution video and advanced features often opt for wired solutions. Choosing the right power source and understanding its implications will contribute significantly to the effectiveness and longevity of your security camera system.
3. Video Quality and Streaming Performance
Video quality and streaming performance are critical factors when choosing between wireless vs wired security cameras. The method of data transmission significantly impacts the resolution, frame rate, reliability, and overall performance capabilities of your surveillance system. Each approach, wired and wireless, offers distinct advantages for different use cases and understanding these nuances is essential for making an informed decision.
Wired security cameras transmit data via physical cables, typically coaxial or Cat5/Cat6 ethernet cables. This direct connection provides a dedicated pathway for video data, resulting in consistent bandwidth and high-resolution streaming. Wireless security cameras, on the other hand, transmit data over Wi-Fi. While offering flexibility in placement and ease of installation, their performance is dependent on the strength and stability of the wireless network. Factors like signal interference, distance from the router, and bandwidth sharing with other devices can affect the video quality and streaming reliability of wireless cameras.
Compression algorithms also play a significant role in video quality and streaming performance. Both wired and wireless systems utilize compression to reduce file sizes for storage and transmission. However, higher compression levels can lead to a noticeable reduction in image quality, particularly in scenes with a lot of motion or detail. Wired systems, with their higher bandwidth capacity, can support less aggressive compression, preserving more detail in the video stream. Wireless systems, especially when bandwidth is limited, may employ more aggressive compression, potentially sacrificing image quality for smoother streaming. Real-time streaming capabilities also differ based on the connection stability. Wired connections offer consistent, uninterrupted streaming due to their dedicated bandwidth, making them ideal for critical surveillance applications. Wireless connections, susceptible to interference and bandwidth fluctuations, can sometimes experience lag or dropped frames, affecting real-time viewing.
Pros and Cons of Wired and Wireless Systems:
Wired:
Pros: Consistent 4K streaming, no bandwidth competition, reliable real-time viewing, supports multiple high-resolution cameras.
Cons: Cable damage can affect quality, limited by physical infrastructure.
Wireless:
Pros: No cable degradation, easy to upgrade individual cameras, mobile-optimized streaming.
Cons: Bandwidth sharing with other devices, potential for signal interference, compression may reduce quality.
Examples of Wired and Wireless Implementations:
Ubiquiti UniFi Protect systems deliver consistent 4K video through wired connections, demonstrating the high-resolution capabilities of wired systems.
Nest Cam IQ can stream 1080p wirelessly but may reduce to 720p during high network traffic, highlighting the impact of bandwidth limitations on wireless cameras.
Professional installations using Cat6 cables support up to 10Gbps for multiple 4K streams, showcasing the bandwidth capacity of wired infrastructure.
Ring cameras automatically adjust quality based on available Wi-Fi bandwidth, illustrating the dynamic adaptation of wireless cameras to network conditions.
Tips for Optimizing Performance:
For Wireless:
Position cameras within optimal Wi-Fi range (typically 100-300 feet).
Use dedicated Wi-Fi networks for security cameras to avoid bandwidth competition.
For Wired:
Use quality cables (Cat5e minimum, Cat6 preferred) for optimal performance.
Test streaming quality during peak network usage times to ensure adequate bandwidth.
The following bar chart visualizes the typical streaming capabilities of wired and wireless security cameras in terms of resolution and frame rate.
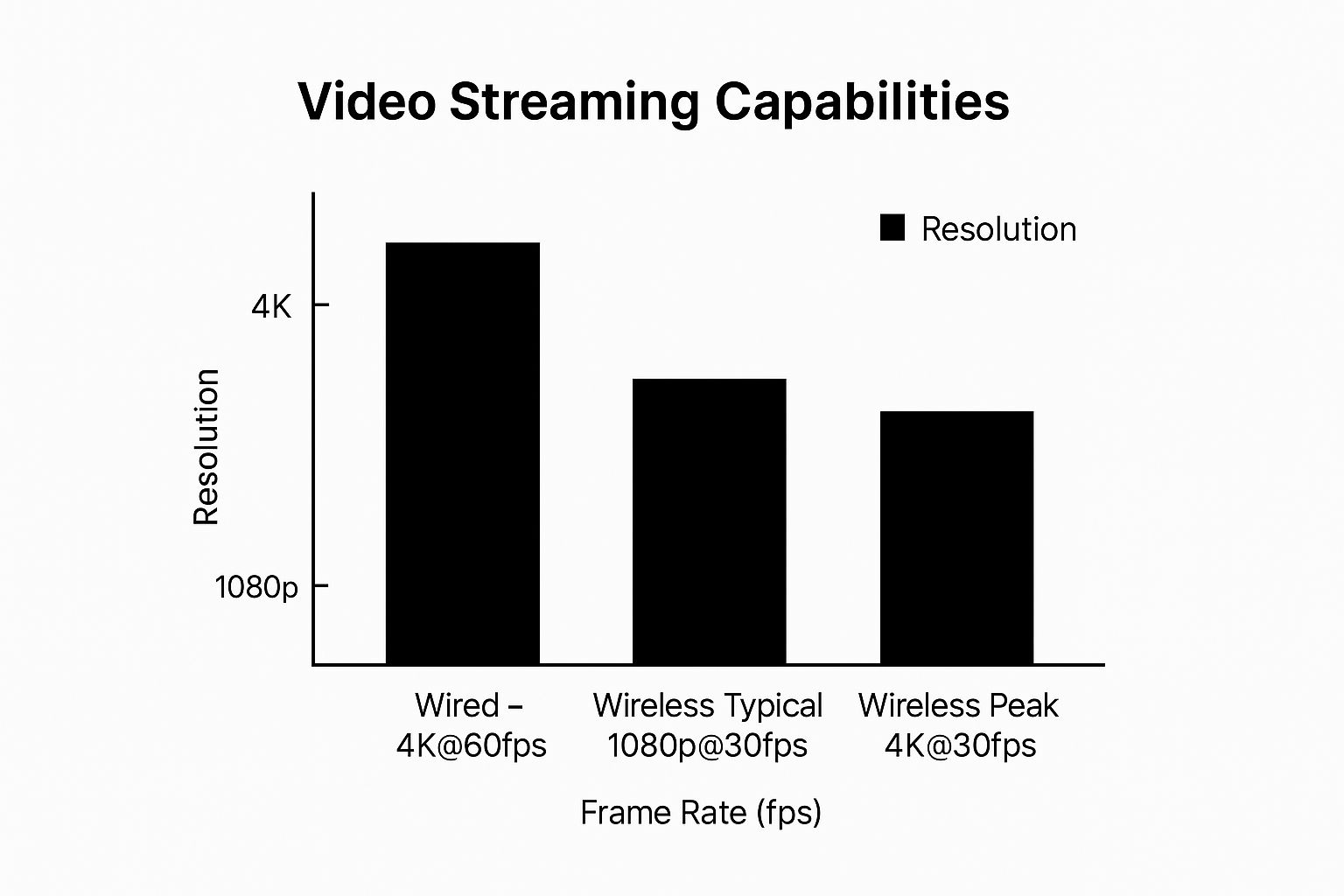
As the chart depicts, wired connections consistently achieve 4K resolution at 60 frames per second (fps), providing the highest quality video. Wireless cameras can typically achieve 1080p at 30fps, but under peak network load, even 4K capable wireless cameras may drop to 30fps or lower resolutions to maintain streaming stability. This reinforces the importance of considering bandwidth requirements when opting for wireless security cameras.
Choosing the right security camera system depends on your specific needs and priorities. If consistent high-resolution video and reliable real-time streaming are paramount, a wired system is the preferred choice. If flexibility and ease of installation are more important, a wireless system may be suitable, provided you are aware of the potential limitations in video quality and streaming performance. By carefully evaluating your requirements and understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each approach, you can make an informed decision that best suits your surveillance needs.
4. Cost Analysis and Total Ownership
When comparing wireless vs wired security cameras, a crucial aspect often overlooked is the total cost of ownership. While the initial sticker price of a camera might seem like the primary expense, a comprehensive cost analysis should encompass installation, maintenance, ongoing operational costs, and potential future expansion. These factors can significantly impact your budget over the long term, making a seemingly inexpensive system quite costly down the line. Understanding these hidden expenses allows for informed decision-making and prevents unexpected financial burdens.

Initial Equipment Costs: Wireless cameras generally have a higher per-unit cost than wired cameras. This is because they incorporate more technology within each unit, such as batteries, Wi-Fi modules, and often, more sophisticated image processing. Wired cameras, on the other hand, benefit from economies of scale, especially when purchasing multiple units for larger systems.
Installation Costs: This is where wireless systems shine. Their DIY-friendly nature often eliminates the need for professional installation, saving hundreds or even thousands of dollars. Wired systems, conversely, almost always require professional installation due to the complexity of running cables, configuring the network video recorder (NVR), and setting up the power supply. This can add a significant upfront cost. For example, a four-camera Hikvision wired system might cost $100-$200 per camera but then incur an additional $500-$1500 for professional installation.
Ongoing Operational Costs: Wireless cameras often require battery replacements, which can add up over time. Some systems also rely on cloud storage for recorded footage, leading to recurring subscription fees. For instance, a Ring wireless system might cost $200-$400 per camera with an additional $3-$10 monthly fee for cloud storage. Wired systems, while generally avoiding battery and subscription costs, might have higher power consumption due to the constantly running NVR. Maintenance costs can vary for both, although wired systems might require more specialized troubleshooting if cable or NVR issues arise. Arlo Pro series, a popular wireless option, can cost $150-$300 per camera with an optional $15 monthly subscription for advanced features.
Scalability Costs: Expanding a wireless system is typically easier and less expensive as it only requires adding new cameras to the network. Expanding a wired system, however, can necessitate additional cabling, potentially requiring professional assistance and increasing costs. A professionally installed 8-camera wired system could range from $1200-$3000 including labor.
Pros and Cons:
Wireless:
Pros: Lower initial installation costs, DIY-friendly installation, no cable infrastructure investment.
Cons: Higher per-camera costs, battery replacement expenses, potential subscription fees.
Wired:
Pros: Lower per-camera costs for large systems, no ongoing battery costs, generally longer equipment lifespan.
Cons: High professional installation costs, infrastructure investment, difficult to relocate cameras.
Tips for Calculating Total Cost of Ownership:
Project Long-Term Costs: Calculate the total cost of ownership over a 3-5 year period. This should include the initial purchase price, installation costs, estimated battery replacements, subscription fees, and potential maintenance expenses.
Consider DIY for Wired Systems (If Skilled): Tech-savvy users can potentially save money by installing wired systems themselves. However, this requires careful planning and a solid understanding of networking and electrical wiring.
Factor in Insurance Discounts: Some insurance companies offer discounts for homes and businesses with professionally installed security systems. This can offset some of the initial installation costs.
Evaluate Storage Options: Compare the costs of cloud storage subscriptions with the cost of setting up a local Network Video Recorder (NVR) for storing footage.
When to Choose Which System: Wireless systems are often a good fit for renters, smaller homes, or situations where running cables is impractical. They offer quick setup and flexibility. Wired systems are generally preferred for larger properties, businesses, or situations where reliability and continuous recording are paramount.
By carefully analyzing the total cost of ownership, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your budget and security needs, whether that be a wireless solution from providers like Ring (Amazon) or Arlo, or a wired system from companies like Hikvision or Dahua. This long-term perspective ensures that your security investment provides value and protection without unexpected financial strain.
5. Security and Vulnerability Assessment
When comparing wireless vs wired security cameras, a crucial factor to consider is the security and vulnerability landscape of each system. Understanding the inherent risks and protection mechanisms is paramount for making informed decisions, especially for sensitive installations. This assessment involves analyzing potential weaknesses, implementing appropriate security measures, and understanding how these vulnerabilities differ between wireless and wired setups. This knowledge is essential for residential homeowners, business owners, and security professionals alike.
Wireless camera systems, while offering flexibility and ease of installation, present unique security challenges. Their reliance on Wi-Fi connectivity introduces vulnerabilities such as signal interference, hacking attempts, and signal interception. Malicious actors can exploit weak Wi-Fi passwords or utilize sophisticated techniques like Wi-Fi jamming to disrupt or disable wireless security systems. For example, professional criminals have been known to employ Wi-Fi jammers to create blind spots during burglaries, effectively neutralizing wireless security cameras. Furthermore, the wireless transmission itself, if not properly encrypted, can be intercepted, potentially exposing sensitive video footage.
Wired camera systems, on the other hand, boast a different security profile. Their physical infrastructure, utilizing cables like Cat5/Cat6, makes them less susceptible to remote hacking and wireless signal interference. However, they are vulnerable to physical tampering and cable cutting. A single cut cable can disable a camera or even an entire section of the surveillance system. Physical access to network equipment also presents a potential point of failure, as tampering with routers or network video recorders (NVRs) could compromise the entire system. For example, there have been documented cases of cable cutting incidents in commercial installations, highlighting the vulnerability of wired systems to physical attacks.
The encryption methods employed by each system also play a significant role in their overall security. Wireless systems often rely on encryption protocols like WPA2 or the more robust WPA3 to secure Wi-Fi transmissions. Reputable brands like Ring and Arlo utilize AES encryption to protect the confidentiality of video data transmitted wirelessly. Wired systems, while inherently more secure against wireless interception, can benefit from network segmentation and isolation techniques. For instance, utilizing VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) on Cat5/Cat6 wired systems allows for isolating security cameras on a separate network, enhancing security and preventing unauthorized access.
Network isolation capabilities also differ between the two systems. Wired systems offer more robust network isolation options, allowing for dedicated networks solely for security camera traffic. This segmentation significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access from other devices on the network. Wireless systems, while offering some isolation through network segmentation features within routers, are generally less isolated due to their reliance on the shared Wi-Fi network.
Choosing between wireless vs wired security cameras depends heavily on the specific security needs and risk assessment of the installation. Wireless solutions offer flexibility and ease of deployment, making them suitable for residential applications, temporary setups for events, or construction site deployments with mobile solar camera trailers. Wired systems, with their enhanced physical security and network isolation capabilities, are often preferred for sensitive installations in businesses, commercial properties, or facilities requiring comprehensive intrusion systems.
Tips for Enhancing Security:
Wireless:
Use WPA3 encryption: This offers the strongest protection against Wi-Fi hacking.
Change default passwords: Immediately change default passwords for cameras, routers, and any network devices.
Enable two-factor authentication: This adds an extra layer of security to access your system.
Consider cellular backup: Some wireless systems offer cellular backup for continued operation in case of internet outage.
Wired:
Protect cable runs: Conceal and protect cable runs to prevent easy access for tampering.
Use tamper-evident conduits: These conduits make it obvious if someone has attempted to access the cables.
Implement network segmentation: Isolate the security camera network using VLANs or dedicated network hardware.
For both Wireless and Wired Systems:
Regular firmware updates: Keep your camera firmware and network equipment updated to patch security vulnerabilities.
Consider backup recording methods: For critical security applications, consider local storage or cloud backup for redundancy.
By understanding the security considerations and implementing the recommended best practices, you can effectively leverage the strengths of each system and mitigate potential risks, ensuring a robust and secure surveillance solution.
6. Scalability and System Expansion
When choosing between wireless vs wired security cameras, scalability and system expansion are crucial factors impacting long-term flexibility and adaptability to evolving security needs. Your initial camera setup might suffice for the present, but future requirements may necessitate adding more cameras to cover new areas or enhance existing surveillance. The ease and cost of this expansion differ significantly between wireless and wired systems. Understanding these differences is essential for making an informed decision that aligns with your current and future security objectives.
Wireless systems offer a plug-and-play approach to expansion, making them attractive for their simplicity. Adding a new camera typically involves connecting it to your existing Wi-Fi network, configuring it through a mobile app, and positioning it within the network's range. This ease of installation translates to minimal wiring costs and allows for flexible repositioning of cameras as needed. Systems like Arlo, for example, support up to 20 cameras on a single base station, while the Ring ecosystem allows for virtually unlimited camera additions within your Wi-Fi coverage area. This flexibility is ideal for homeowners and small businesses looking to gradually expand their security coverage. Imagine starting with a single doorbell camera and then easily adding cameras to monitor your driveway, backyard, or other vulnerable areas as your budget and security needs evolve. This convenience makes wireless systems particularly appealing for renters or those hesitant about extensive wiring.
However, the convenience of wireless expansion comes with limitations. The most significant constraint is network bandwidth. As you add more wireless cameras, the demand on your Wi-Fi network increases, potentially leading to congestion and degraded performance, including lag, dropped frames, and reduced video quality. This is especially true with higher-resolution cameras. For instance, multiple 4K wireless cameras streaming simultaneously can quickly overwhelm a standard home Wi-Fi network. Moreover, wireless range can be a limiting factor. Obstacles like thick walls or metal structures can obstruct the signal, restricting placement options. While mesh Wi-Fi systems can extend coverage for larger deployments, they add complexity and cost to the overall system.
Wired systems, on the other hand, offer a more robust and scalable solution for larger deployments. While the initial setup requires more planning and investment in infrastructure, wired systems provide consistent performance even with a large number of cameras. Ubiquiti UniFi Protect, for example, supports 50+ cameras on enterprise-grade wired systems. Traditional DVR systems, though limited by the number of available ports (typically 4, 8, or 16 cameras), offer a reliable wired solution for smaller installations. The centralized management capabilities of wired systems also simplify administration and maintenance for large-scale deployments. This makes wired systems ideal for businesses, construction sites, and event venues requiring extensive and reliable surveillance. Consider a construction site manager needing to monitor multiple access points and equipment storage areas; a wired system provides the consistent performance and scalability necessary for comprehensive security.
The primary drawback of wired systems lies in the cost and complexity of expansion. Adding cameras in new locations requires running cables, which can be expensive and disruptive, especially in existing structures. This necessitates careful planning and ideally involves installing extra cable runs during initial construction or renovation. For example, a homeowner building a new house should consider future security needs and pre-wire for potential camera locations, even if they don't plan on installing a full system immediately. This foresight can significantly reduce the cost and hassle of future expansion.
Choosing between wireless and wired security cameras for scalability depends on your specific needs and circumstances. For residential users with limited camera needs and a focus on easy installation, wireless systems offer an attractive option. However, for larger deployments requiring robust performance and centralized management, wired systems are the preferred choice, despite the higher initial investment. Evaluating future security needs and planning accordingly is crucial for choosing the right architecture and maximizing long-term value. For wireless systems, carefully plan Wi-Fi coverage and consider mesh Wi-Fi for larger deployments. For wired systems, invest in adequate infrastructure planning and consider installing extra cable runs during initial construction to accommodate future expansion. By considering these factors, you can build a security system that adapts to your changing needs and provides reliable protection for years to come.
Wireless vs Wired Cameras: Key Feature Comparison
⭐ Feature / Consideration | 🔄 Implementation Complexity | ⚡ Resource Requirements | 📊 Expected Outcomes | 💡 Ideal Use Cases | 📊 Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Installation and Setup Complexity | Wireless: Low (15-60 min/camera), Wired: High (2-8 hrs full system) | Wireless: Minimal tools, no cabling; Wired: Cabling, professional install | Wireless: Flexible placement, quick setup; Wired: Stable connection | Wireless: DIY, quick deployment; Wired: Permanent setups, large systems | Wireless: Easy setup ⭐, Wired: Reliable connection 🔄 |
Power Source and Reliability | Wireless: Battery management, Wired: Electrical setup with UPS option | Wireless: Batteries, solar; Wired: Power over Ethernet (PoE), UPS | Wireless: Portable, battery-dependent; Wired: Continuous power, no battery | Wireless: Remote or hard-to-wire locations; Wired: Constant power needs | Wireless: Portable during outages ⚡, Wired: Stable power supply 📊 |
Video Quality and Streaming Performance | Wired: Complex cabling, Wireless: Network optimization | Wired: Quality cables (Cat5e/Cat6), Wireless: Strong Wi-Fi network | Wired: Consistent 4K@60fps; Wireless: Up to 1080p@30fps typical | Wired: High-res, multi-camera deployments; Wireless: Mobile, flexible setups | Wired: High-quality stable streaming ⭐, Wireless: Easy upgrades 💡 |
Cost Analysis and Total Ownership | Wireless: Lower install cost, Wired: Higher install cost and labor | Wireless: Higher per-camera cost, battery; Wired: Infrastructure, professional install | Wireless: Higher ongoing battery/subscription cost; Wired: Lower maintenance | Wireless: Budget-conscious, DIY users; Wired: Large-scale, long-term investment | Wireless: Lower upfront cost ⚡, Wired: Cost-effective at scale 📊 |
Security and Vulnerability Assessment | Wireless: Network security setup; Wired: Physical protection | Wireless: Encryption, Wi-Fi security; Wired: Cable protection, VLANs | Wireless: Medium risk of interference/hacking; Wired: High physical security | Wireless: Residential or flexible sites; Wired: Sensitive or enterprise environments | Wireless: Encrypted wireless ⭐, Wired: Difficult to hack physically 🔄 |
Scalability and System Expansion | Wireless: Easy add/remove; Wired: Infrastructure planning | Wireless: Network capacity, mesh Wi-Fi; Wired: Cabling, ports | Wireless: Up to 20 cameras typical; Wired: 50+ cameras supported | Wireless: Small to medium setups needing flexibility; Wired: Large deployments | Wireless: Flexible expansion ⚡, Wired: Large-scale stability 📊 |
Making the Right Choice for Your Security Needs
Choosing between wireless vs wired security cameras is a crucial decision for any security-conscious individual or business. This article has explored six key aspects of this decision: installation complexity, power source reliability, video quality and streaming performance, cost analysis, security vulnerabilities, and system scalability. Mastering these concepts empowers you to create a surveillance system tailored to your precise needs, whether it's for your home, business, construction site, or special event. The right system not only enhances security but also provides peace of mind, allowing you to focus on what matters most.
The ideal security solution isn't one-size-fits-all. While wireless cameras offer flexibility and ease of installation, wired systems provide superior reliability and performance. Carefully weigh these factors against your budget and technical capabilities. Ultimately, understanding the nuances of wireless vs wired security cameras enables you to make an informed decision that maximizes your protection and investment.
Looking for expert guidance in navigating the world of wireless vs wired security cameras? PCI Audio-Video Security Solutions offers comprehensive solutions, including both wireless and wired options, designed to meet diverse security requirements. Visit PCI Audio-Video Security Solutions today to explore how our team can help you design and implement a robust security system perfectly suited to your needs in 2025 and beyond.
Article created using [Outrank](https://outrank.so)







Comments